Understanding Binocular Magnification: A Practical Guide [2024]
Binocular magnification is a key specification when it comes to choosing the right binoculars for your needs. In effect it is a measure of how much larger an object appears when viewed through the binoculars, as compared to seeing it with the naked eye.
Binocular magnification is an important binocular number and you need to keep it on your list when shopping for a new pair of binoculars. Let me go into its definition, calculation, and the impact it has on your viewing experience.
So whether you’re a novice birdwatcher looking to buy your first binoculars or an avid traveler wanting to buy a compact binocular, you will have enough insight into binocular magnification to make an informed choice!
This site participates in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program designed to give sites like ours a way to earn advertising fees by linking to products on Amazon.com at no additional cost to you. I appreciate your support. Thank you!
What is Binocular Magnification?
Binocular magnification is the extent to which an object appears larger when viewed through binoculars compared to the naked eye. Binocular magnification is an important specification used to describe binoculars and is critical in determining the level of detail and clarity you can achieve during observation.
Binocular Magnification Calculation
Binocular magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by the focal length of the eyepiece lens. The focal length is the distance between the lens and the point where the image is formed.
Given as the first number in a binocular description (e.g., 7×35, 10×50), magnification is the ratio of the focal length of the objective divided by the focal length of the eyepiece.
WIKIPEDIA
For example, if the objective lens of the binoculars have a focal length of 200mm and the eyepiece have a focal length of 25mm, the binocular magnification would be 8x (200/25).
It also means that if you are 100′ away from an object, say a bird, with 10x binoculars you would see the same details of the bird as you would see from a distance of 10′ without the binoculars.
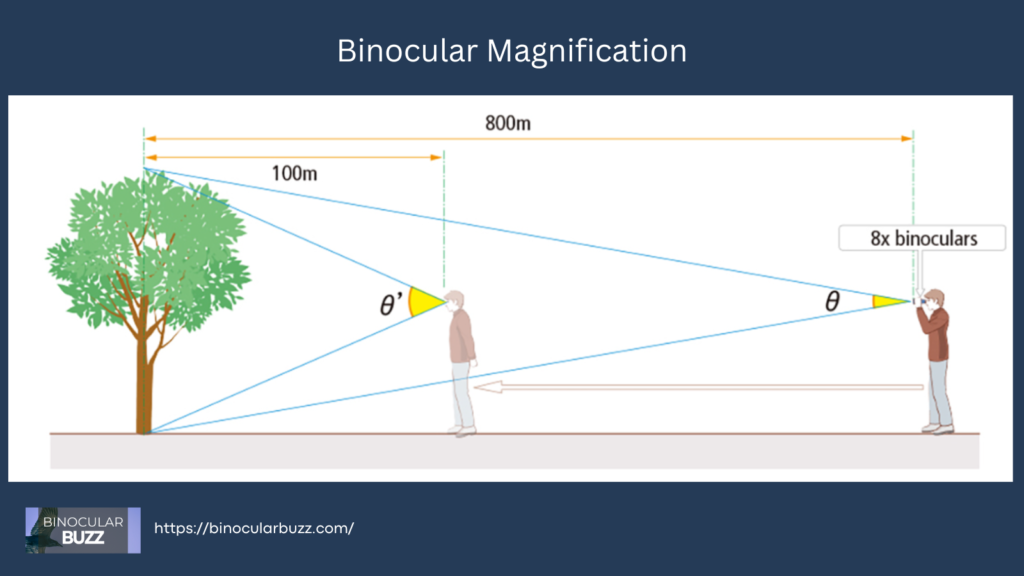
Image Courtesy NIKON
Implications of Binocular Magnification Levels
While higher magnification may seem desirable, it comes with implications on image quality, field of view, image stability, portability, etc.
Image Quality
Higher magnification can have both positive and negative effects on image quality.
- Detail: With higher magnification, you can observe finer details that may otherwise be invisible to the naked eye. As such higher binocular magnification is useful when precision is required, such as in scientific research or wildlife observation.
- Image degradation: However, as magnification increases, the image quality may deteriorate. This can result in a loss of sharpness, clarity, and color accuracy.
- Lens quality: Lenses with high-quality glass and coatings can minimize distortions and aberrations, giving you clearer images.
Field of View
Field of view is the width of the view visible through the binoculars from a distance of 1000′. Higher magnification typically results in a lower field of view.
- Field of View: As magnification increases, the field of view tends to become narrower. A lower magnification, on the other hand may give you a wider field of vision.
- Trade-off: It’s important to strike a balance between magnification and field of view based on your specific needs.
- For example a wider field of view and a lower magnification may be perfect for observing birds in flight but a narrower field of view and a higher magnification is desirable for observing birds at a feeder in your backyard.
Image Stability
Image Stability becomes increasingly important as magnification levels rise. Here’s why:
- Shaky Images: Higher magnification can amplify even the slightest hand movements, resulting in shaky or blurred images. Very high magnification binoculars may require the use of tripods or image stabilization technology.
Portability
Portability usually reduces as binocular magnification increases. Here’s why:
- Weight and Portability: Quite often, binoculars with higher magnification and objective lens diameter tend to be larger and heavier.
- Trade-off: As such you will need to make a trade-off between binocular magnification level and objective lens diameter on one hand and the size, weight and portability on the other.
- It all depends on the “intended use” of the binoculars.
Exit Pupil
- Higher magnification results in a smaller exit pupil, impacting visibility in low-light conditions. Choose lower binocular magnification for a larger exit pupil, enhancing image brightness and clarity.
Key Takeaways – Binocular Magnification
- Determines how much larger an object appears when viewed through binoculars.
- Is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by the focal length of the eyepiece.
- Is not the only factor to be considered when buying a binocular. You need to consider other factors such as field of view, image stability, portability, etc.
Beyond Binocular Magnification
The most important binocular numbers are expressed as binocular magnification and objective lens size. For example a pair of 8×42 binoculars have a binocular magnification of 8x and an objective lens diameter of 42mm.
Objective Lens Size
The objective lens size, generally ranging from 20mm to 50mm, influences light-gathering capability. Larger objective lenses can gather more light and provide higher image clarity and quality, even in low light conditions, such as dawn or dusk.
Importance of Objective Lens Size in Binoculars
The objective lens size plays a critical role in determining the performance and viewing experience of binoculars. Here’s why it’s important and how it affects the overall viewing experience:
- Light Gathering Capability: The objective lens is responsible for gathering light and directing it to the eyepiece. A larger objective lens diameter allows more light to enter the binoculars, resulting in brighter images, especially in low-light conditions such as dawn, dusk, or overcast days. This enhanced light gathering capability improves visibility and clarity, making it easier to discern details and colors in dimly lit environments.
- Image Brightness and Contrast: With a larger objective lens, binoculars can produce brighter images with better contrast. Brighter images enhance visibility and make it easier to distinguish subtle features, textures, and colors, leading to a more immersive viewing experience.
- Magnification Capability: The size of the objective lens also influences the magnification capability of binoculars. Larger objective lenses typically accommodate higher magnification levels, allowing users to observe distant objects with greater detail and clarity. This is particularly beneficial for activities such as birdwatching, wildlife observation, or stargazing, where observing fine details is important.
- Field of View: While objective lens size primarily affects image brightness and magnification, it indirectly impacts the field of view (FOV). Binoculars with larger objective lenses tend to have wider FOVs, providing a broader perspective and making it easier to track moving objects or scan large areas.
- Size and Weight: It’s worth noting that larger objective lenses generally result in bulkier and heavier binoculars. While this may enhance light gathering capability and image quality, it can also affect portability and ease of use.
The objective lens size influences the performance and viewing experience of binoculars by impacting light gathering capability, image brightness, magnification capability, field of view, and overall size and weight. Choosing the right objective lens size based on your intended use is therefore important too.
Eyepiece Design
Different eyepiece designs affect magnification power and overall viewing experience. Common designs include:
- Standard Eyepiece: Binoculars with standard eyepieces typically offer a magnification power of 8X or 10X. These magnifications are well-suited for general use, such as nature observation or casual stargazing. They provide a good balance between magnification and stability, ensuring a steady view without excessive shaking.
- Zoom Eyepiece: Some binoculars feature a zoom eyepiece, allowing you to adjust the magnification within a certain range (e.g., 8X to 24X). This versatility can be advantageous in situations where the desired level of magnification may vary. However, it’s important to note that zoom eyepieces may sacrifice some image quality compared to binoculars with fixed magnification.
- Wide-Angle Eyepiece: Binoculars equipped with wide-angle eyepieces provide a wider field of view, allowing users to observe a broader scene. While the magnification power may not be as high as with other eyepiece designs, the enhanced field of view can be beneficial for activities such as hunting or hiking, where you need a panoramic view.
What is the Best Binocular Magnification for Me?
I think, by now, you have understood that a binocular is not better simply because it has a higher magnification. It is all about what are you going to use the binoculars for.
Below is a table to help you choose the perfect magnification for your preferred activity.
| Magnification Level | Objective Diameter | Suggested Activity |
|---|---|---|
| 6x – 7x | 25mm – 30mm | Hiking, Camping, Sporting Events, Concerts |
| 6x – 7x | 32mm – 35mm | Birding, Travel, Sporting Events, Concerts, General Purpose |
| 8x – 9x | 25mm – 30mm | Hiking, Camping, Sporting Events, Concerts |
| 8x – 9x | 32mm – 35mm | Birding, Travel, Sporting Events, Concerts, General Purpose |
| 8x – 9x | 40mm – 42mm | Birding, Travel, General Purpose |
| 10x – 12x | 25mm – 30mm | Hiking, Camping, Sporting Events, Concerts |
| 10x – 12x | 32mm – 35mm | Birding, Travel, Sporting Events, Concerts |
| 10x – 12x | 40mm – 42mm | Birding, Travel, Hunting |
| 10x – 12x | 50mm – 56mm | Birding, Astronomy, Hunting, Law Enforcement |
| 15x – 16x | 32mm – 35mm | Travel, Sporting Events, Concerts |
| 15x – 16x | 50mm – 56mm | Astronomy, Hunting, Law Enforcement |
| 20x – 25x | 50mm – 56mm | Astronomy, Seawatch, Law Enforcement |
| 20x – 25x | 60mm | Astronomy, Seawatch, Law Enforcement |
| 20x – 25x | 70mm | Astronomy, Seawatch, Law Enforcement |
| 20x – 25x | 80mm | Astronomy, Seawatch, Law Enforcement |
| 20x – 25x | 100mm | Astronomy, Seawatch, Law Enforcement |
Other Considerations
Apart from the specific activity, there are a few additional factors to keep in mind when choosing the right magnification:
- Comfort: Consider the weight and size of the binoculars. Make sure they are comfortable to hold for extended periods.
- Image Quality: Look for high-quality optics with coatings that enhance brightness, contrast, and color fidelity. This will ensure a clear and detailed view of your subject.
- Budget: Determine your budget and look for options within that range. There are numerous reputable brands like Nikon, Celestron, and Vortex that offer a range of magnifications to suit different budgets.
Bottom Line: Binocular Magnification
Binocular magnification is pivotal for long-distance viewing, but higher magnification isn’t always better. Tailor your choice to your specific needs, considering factors like field of view, image stability, and intended use.
Take the time to explore different options and find what enhances your viewing experience. Enjoy the long-distance view with the perfect binocular magnification!